
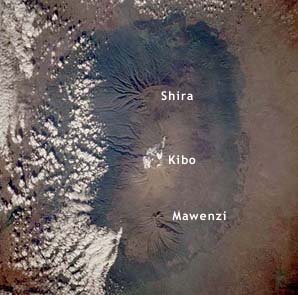
 NASA Space Shuttle Photo Larger Image (131k JPEG) |
This image, taken by astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle, shows Mt. Kilimanjaro and its three volcanic cones. North is to the right. While Kibo has not been active in modern times, steam and sulfur are occassionally emitted. The crater atop Kibo is 1.5 mi. (2.25 km) wide. Shira, topped by a broad plateau, has experienced significant erosion while Mawenzi is a steep, rocky peak with 1,600 ft (0.5km) - 4,900 ft (1.5km) cliffs on all sides. Mawenzi is the third highest peak in Africa. |

