|
|
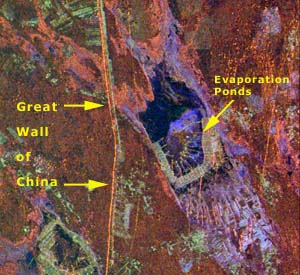
Segments of the Great Wall of China can be seen in images from the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) instrument flown on the Space Shuttle in April 1994. This enlargement shows a section of the Wall in a desert region about 730 km (440 mi) from Beijing. The orange line indicates portions of the Wall dating to the 15th Century. Other sections of the Wall are many centuries older. Here the Wall ranges from 5 to 8 m (16 to 26 ft) high. The angular features at center of the image are salt evaporation ponds. The image is presented in false color, with different colors representing different frequencies and polarizations of the radar signals. |